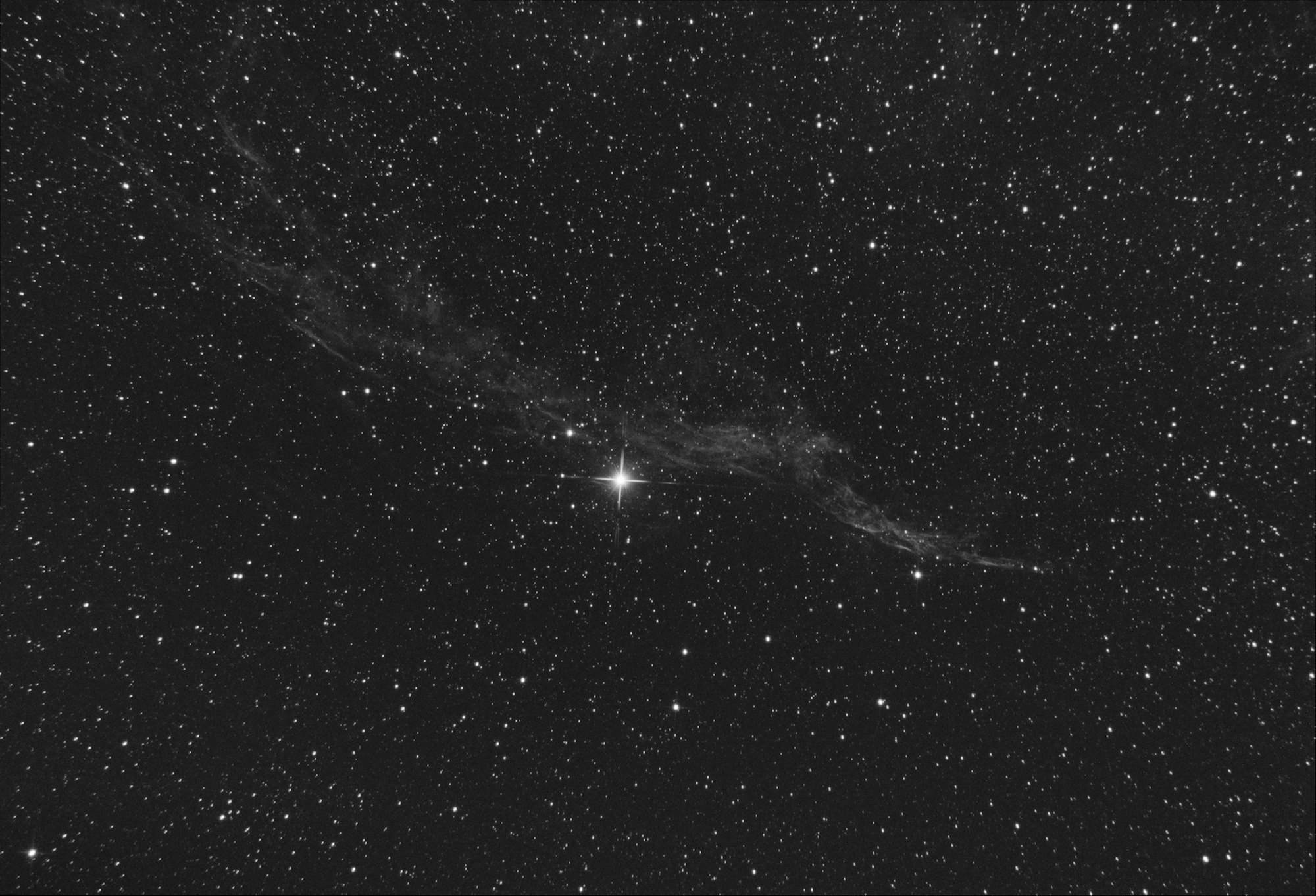
The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus. It constitutes the visible portions of the Cygnus Loop (radio source W78, or Sharpless 103), a large but relatively faint supernova remnant. The source supernova exploded circa 3,000 BC to 6,000 BC, and the remnants have since expanded to cover an area roughly 3 degrees in diameter (about 6 times the diameter, or 36 times the area, of the full moon). The distance to the nebula is not precisely known, but Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer(FUSE) data supports a distance of about 1,470 light-years.
The Hubble Space Telescope captured several images of the nebula. The analysis of the emissions from the nebula indicate the presence of oxygen, sulfur, and hydrogen. This is also one of the largest, brightest features in the x-ray sky. (Source: Wikipedia)
Technical Details
Dates: 30/6/2018
Location: Cologne, Germany
Imaging Telescope: 8″ GSO f/4 (Carbon Tube)
Imaging Camera: ASI294 MC
Filter: Baader Planetarium H-Alpha (35 nm)
Mount: Skywatcher EQ-6
Guiding Telescope: TSO OAG
Guiding Camera: QHY 5L-II
Integration: 20 x 3,3 min. (Gain: 130)
Software: PixInsight, EKOS, OpenPhDGuiding, INDI
Plate Solution

(Source: astrometry.net)